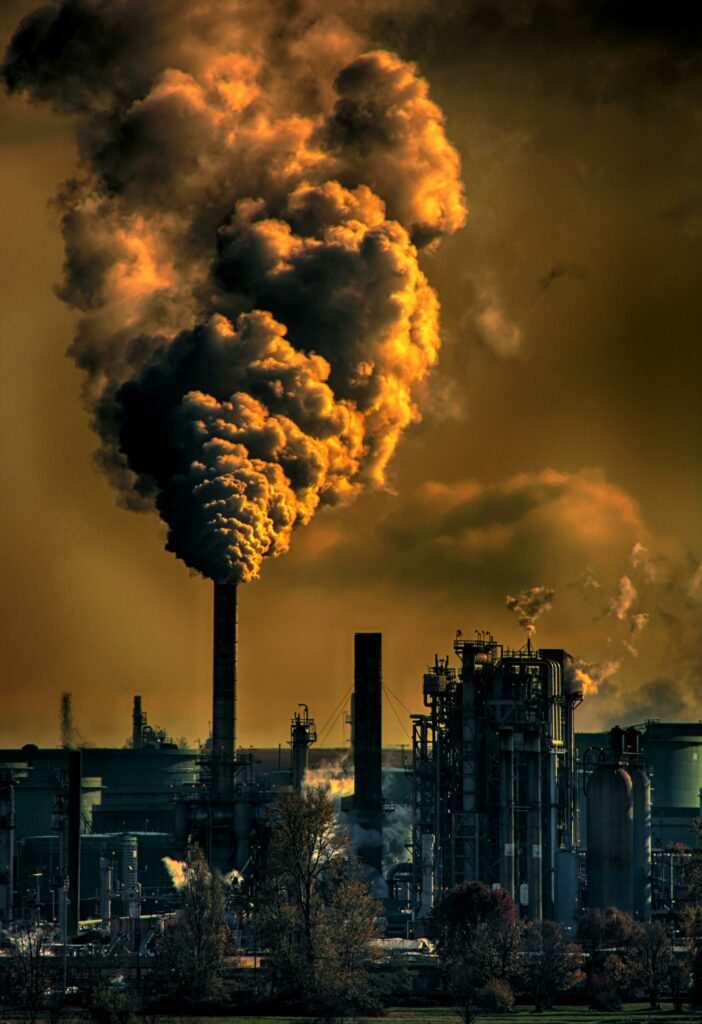

It’s extremely hard to completely rid yourself of toxic chemicals or pollutants as, sadly, it surrounds us everyday. Pollution can be caused by natural sources like volcanic ash or wildfires that affect our air quality or it can be human made like run off from factories. Our skin, lungs and digestive system are instrumental in getting good things in but unfortunately, even with our natural barriers the bad can sneak in too, creating havoc to our ingrained systems.
Air pollution is a major crisis to our health and skin. They trigger oxidative stress which can eventually lead to cell death. The free radicals or reactive oxidative stress (ROS) are molecules that contain unpaired electrons making them highly reactive. This can occur during normal metabolic processes or from environmental factors like pollution. These free radicals can attack the fatty acids in cell membranes which affect the integrity of the cell.
They can also cause protein oxidation which accelerates aging and can increase the risk of neurodegenerative and cardiovascular disease. Protein oxidation affects the structure of proteins and consequently their biological functions. Antioxidants fight against free radicals and are necessary to combat the unstable reactivity of free radicals. Antioxidants are found in fruits and vegetables. When there’s an imbalance between the reactive oxygen species (ROS)and the antioxidants to neutralize them, oxidative stress occurs.
Inflammation is also increased with pollution as pollutants can trigger the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines which can exacerbate conditions like atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Collagen breakdown is a big component in visible signs of aging. Pollutants can increase the degradation of collagen and inhibit its production. This can directly lead to wrinkled, sagging, dull skin. Certain pollutants have also been linked to acne.
Some pollutants are carcinogenic and can be carcinogenic with the right amount of exposure.
Examples Of Pollutants That Can Affect The Skin
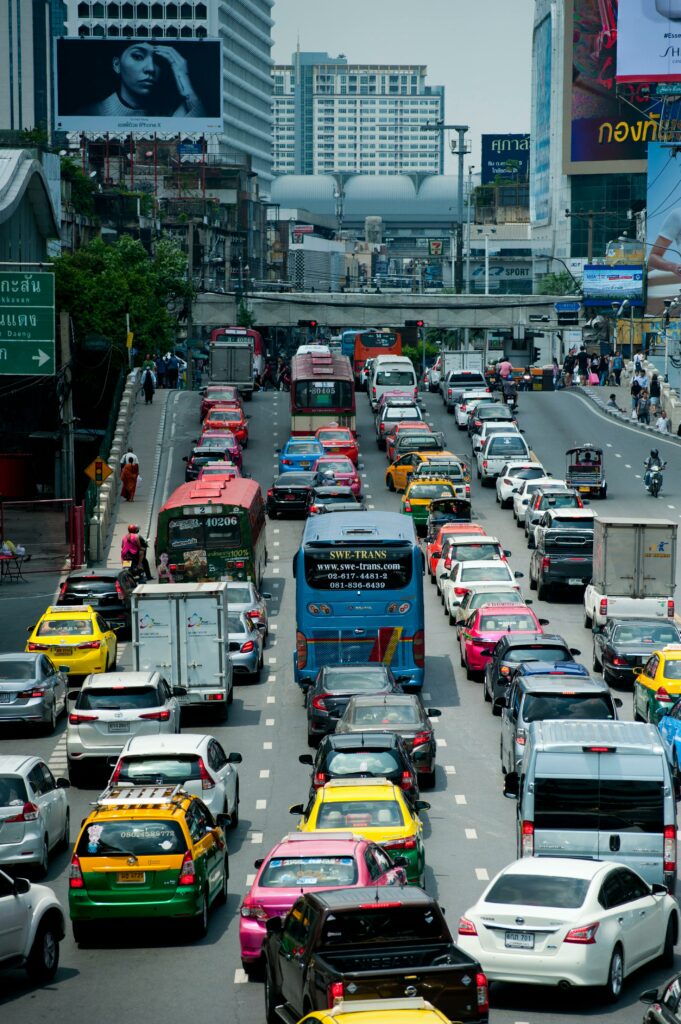

- Particulate matter which can be found in car emission, industrial and construction pollutants such as burning waste, production of chemical, pharmaceuticals, combustion of fossil fuels etc. All of this can cause inflammation to the lungs and eyes.
- Ozone like smog in the air from a mixture of chemicals, pollutants, car exhaust. Again this is sometimes an unavoidable pollutant that overtime can damage our lungs and cause oxidative stress.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are formed when there’s an incomplete combustion of organic matter like fossil fuel or tobacco. Can cause oxidative stress to the body when exposed. Can be found in air, water, soil and foods. Lung, skin and bladder cancer have been associated with long term exposure to high levels of PAH. It’s also been shown to have adverse effects to the reproductive and immune systems.
- Nitrogen dioxide is a common pollutant in the air that typically derives from power plants, vehicle exhaust and industrial processes. Nitrogen dioxide can turn into reactive nitrogen species and cause oxidative stress.
- Sulfur dioxide also comes typically from industrial work and power plants and is emitted from burning fossil fuel. This contributes to both respiratory and oxidative stress.
- Volatile organic compounds are carbon-containing compounds that are easily evaporated in the air at room temperature. Can be found in vehicle exhaust, glues, paints, some cleaning products, cigarettes, formaldehyde which can be found in carpets, wood and furniture. These contribute to indoor and outdoor pollution and can contribute to headaches, respiratory irritation and several other health concerns.
- Phthalates are often used in plastics to make them more flexible and durable. Phthalates have been linked to disruption in cellular homeostasis by interfering with the balance of antioxidants and ROS causing oxidative stress. It has also been seen to increase inflammation and cause dysfunction in our cell’s mitochondria (responsible for energy production) which leads to oxidative stress.
Vulnerable Populations
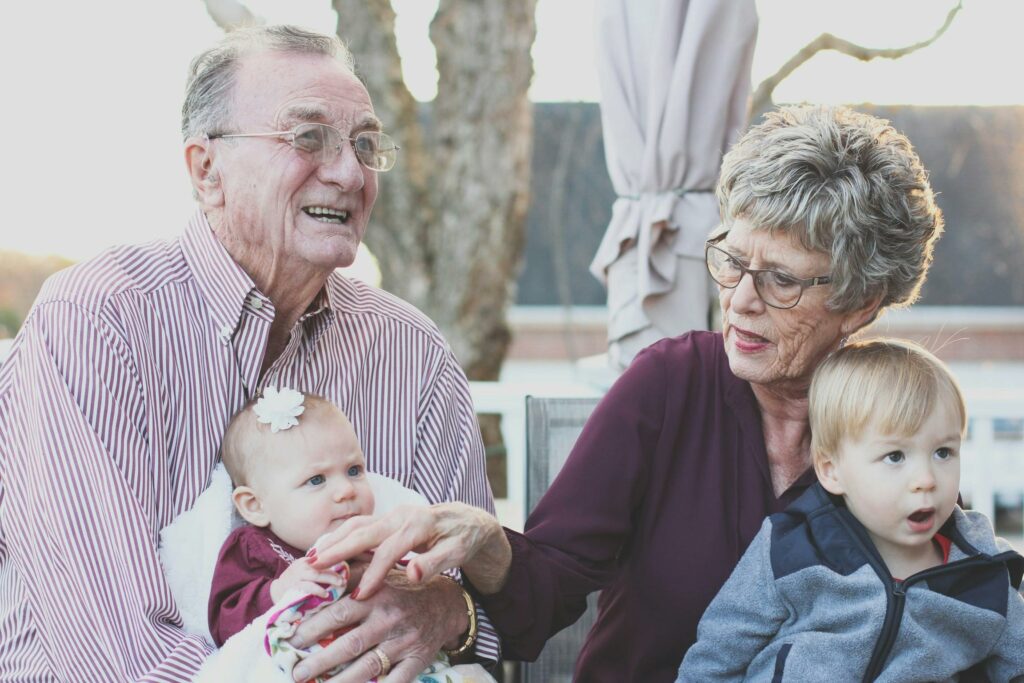

- Elderly-have poor immune systems and are more prone to pollutants causing detrimental respiratory and cardiovascular damage.
- Children– organs are still developing and they tend to have increased respiratory rates which causes them to take in more pollutants. Exposure to pollutants during critical points in growth can do life long damage.
- Pregnant– exposure to certain pollutants during pregnancy can put the fetus at risk for low birth weight, preterm deelivery or developmental issues.
- Pre-existing Health Conditions– when exposed to pollutants, conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cardiovascular conditions or weakened immune system can be exacerbated and cause destruction to one’s health.
- Low-Income families– may live near industrial areas, highways and areas with poor air quality.
- Individuals who live in urban communities– those in cities or highly populated areas with lots of traffic may be exposed more to pollutants than those in rural areas.
How To Combat Pollutants

Combating pollutants is possible but will need the cooperation of individuals, community and governing engagement to make lasting changes. Some changes that can be done are:
- Governing bodies can enforce strict emission standards for vehicles, industries, and other sources of pollutants. With all the research of the sometimes irreparable damage pollution causes, reducing our pollutant load should be at the top of the list of priorities.
- Advances in solar, wind and hydropower are imperative to reduce reliance on fossil fuel. More advances and investments should be made in controlling and reducing the emissions from vehicles and industrial plants.
- Use public transportation, cycle, carpool more often to reduce vehicle emission.
- Focus should be on planting more trees rather than cutting them down to purify our air and absorb pollutants.
- Check the Air Quality Index (AQI) in your city and wear proper protective measures based on reading
- Use air purifiers indoor
- Recycle and practice proper hazardous disposal
- Avoid smoking/second hand smoking
- Use skincare that protects against pollutants like antioxidants and ceramides.
- Continuously read and research ingredients, household products etc that cause toxic build up and a release of pollutants. Try to swap with “green friendly” products that also get the job done!
Also Read: Flowing Clarity: A Deep Dive Into Tap Water Quality
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3155788/




You must be logged in to post a comment.